Inflammation is a natural response by your body’s immune system to injury or infection. However, chronic inflammation can lead to various health issues, including heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. Adopting an anti-inflammatory diet can play a crucial role in promoting overall wellness and reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
Understanding Inflammation
Inflammation is your body’s way of protecting itself. When you get injured or infected, your immune system sends out white blood cells to surround and protect the area. This results in redness, warmth, and swelling. While this acute inflammation is beneficial, chronic inflammation occurs when this response lingers, leaving your body in a constant state of alert. Over time, chronic inflammation can damage healthy tissues and organs.
Benefits of an Anti-Inflammatory Diet

An anti-inflammatory diet focuses on consuming foods that reduce inflammation and avoiding those that trigger it. Benefits include:
- Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases: Lowering inflammation can decrease the risk of heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers.
- Improved Digestive Health: This diet promotes a healthy gut, enhancing digestion and nutrient absorption.
- Enhanced Mood and Energy Levels: Balanced blood sugar levels and reduced inflammation can lead to better mood stability and increased energy.
Key Components of the Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Incorporating specific foods into your diet can help combat inflammation:
1. Fruits and Vegetables
Rich in antioxidants, fruits and vegetables neutralize harmful free radicals in the body. Aim for a colorful variety to ensure a broad spectrum of nutrients.

- Berries: Blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries are high in anthocyanins, which have anti-inflammatory effects.
- Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and collard greens are packed with vitamins and minerals that combat inflammation.
- Cruciferous Vegetables: Broccoli, cauliflower, and Brussels sprouts contain sulforaphane, a compound that reduces inflammation.
2. Healthy Fats
Not all fats are bad. Healthy fats can reduce inflammation and support heart health.

- Olive Oil: Extra virgin olive oil is rich in monounsaturated fats and oleocanthal, which have anti-inflammatory properties.
- Avocados: Packed with monounsaturated fats, fiber, and antioxidants, avocados help reduce inflammation.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds provide omega-3 fatty acids and fiber.
3. Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3s are essential fats that your body cannot produce on its own. They have potent anti-inflammatory effects.
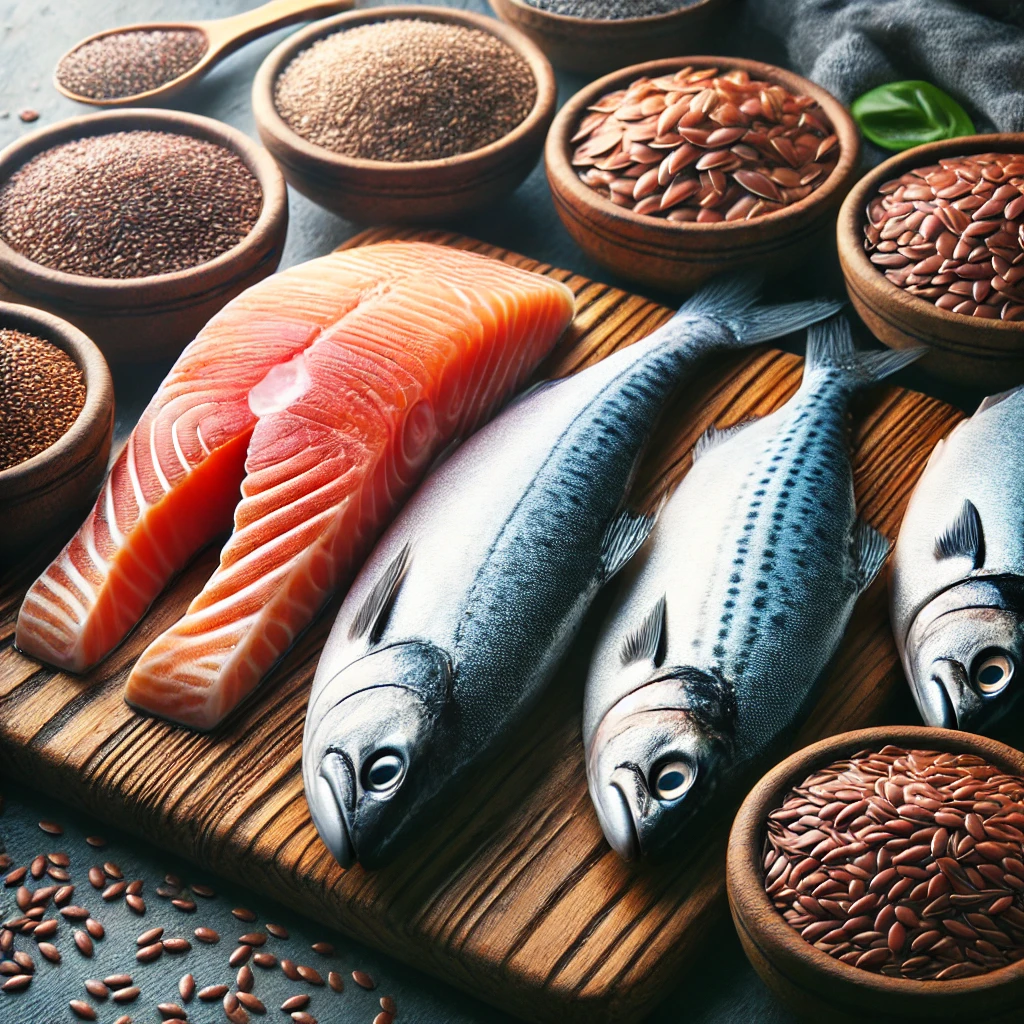

- Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, sardines, and tuna are excellent sources of omega-3s.
- Flaxseeds and Chia Seeds: These seeds are plant-based sources of omega-3s.
4. Whole Grains
Unlike refined grains, whole grains retain their fiber and nutrients, helping to reduce inflammation.
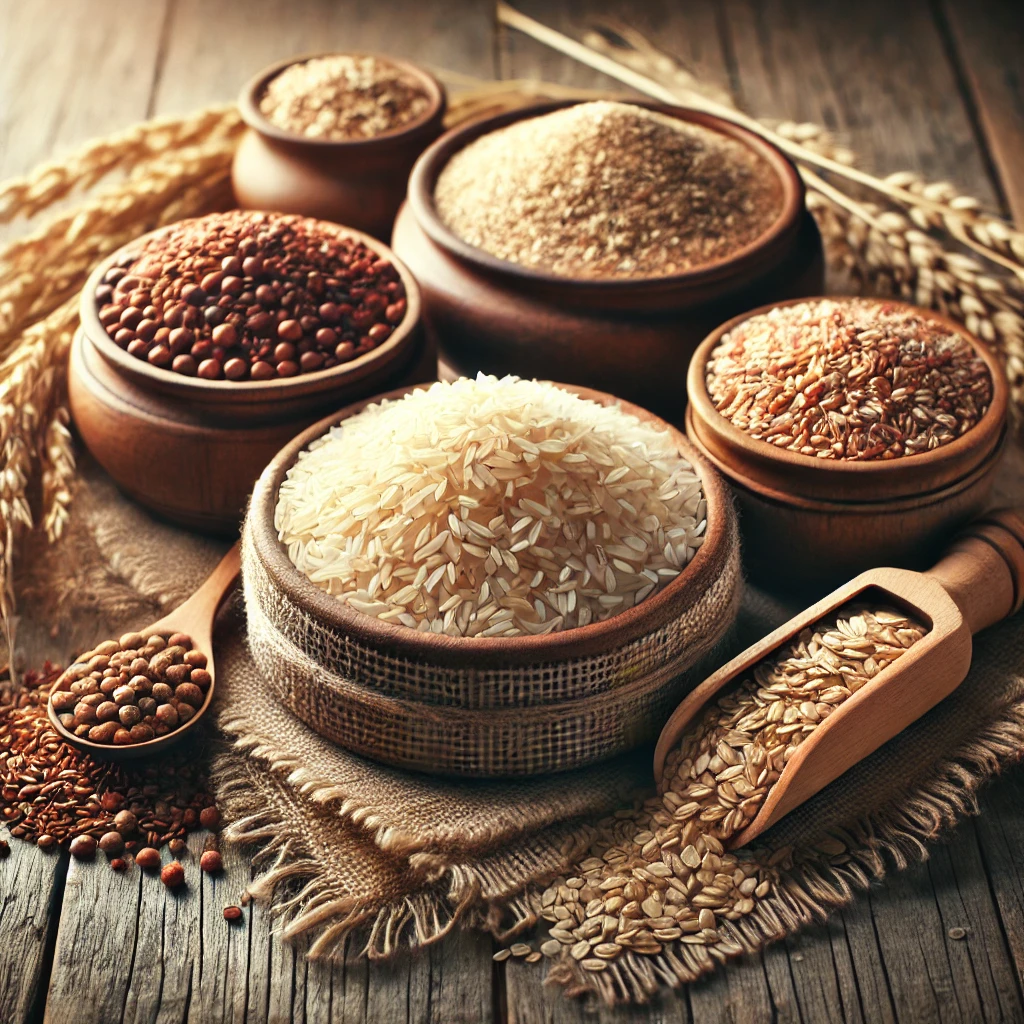

- Brown Rice: A good source of fiber and minerals.
- Quinoa: A complete protein that provides all nine essential amino acids.
- Oats: Rich in beta-glucan, a type of soluble fiber with anti-inflammatory benefits.
5. Herbs and Spices
Many herbs and spices have compounds that fight inflammation.
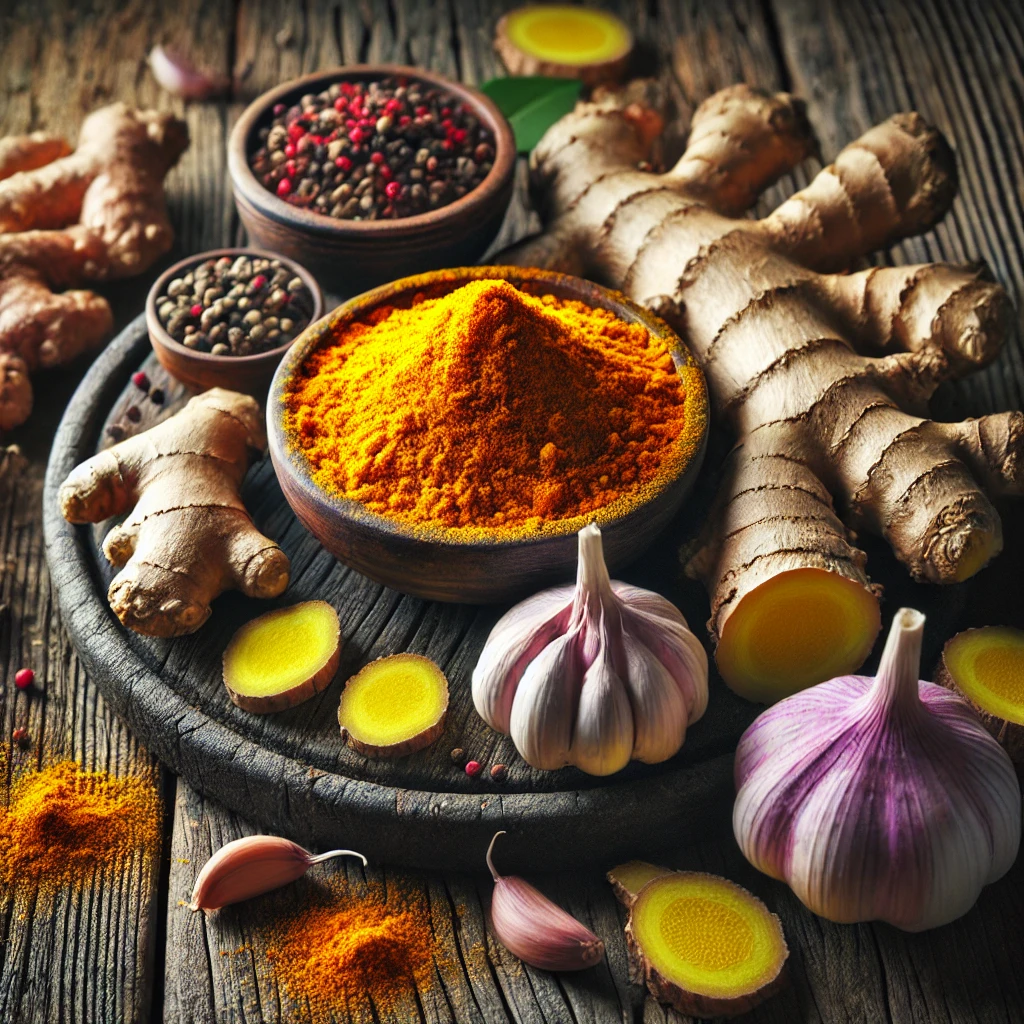

- Turmeric: Contains curcumin, a powerful anti-inflammatory compound.
- Ginger: Known for its ability to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Garlic: Its sulfur compounds can inhibit inflammatory pathways.
Foods to Avoid
Certain foods can promote inflammation and should be limited:
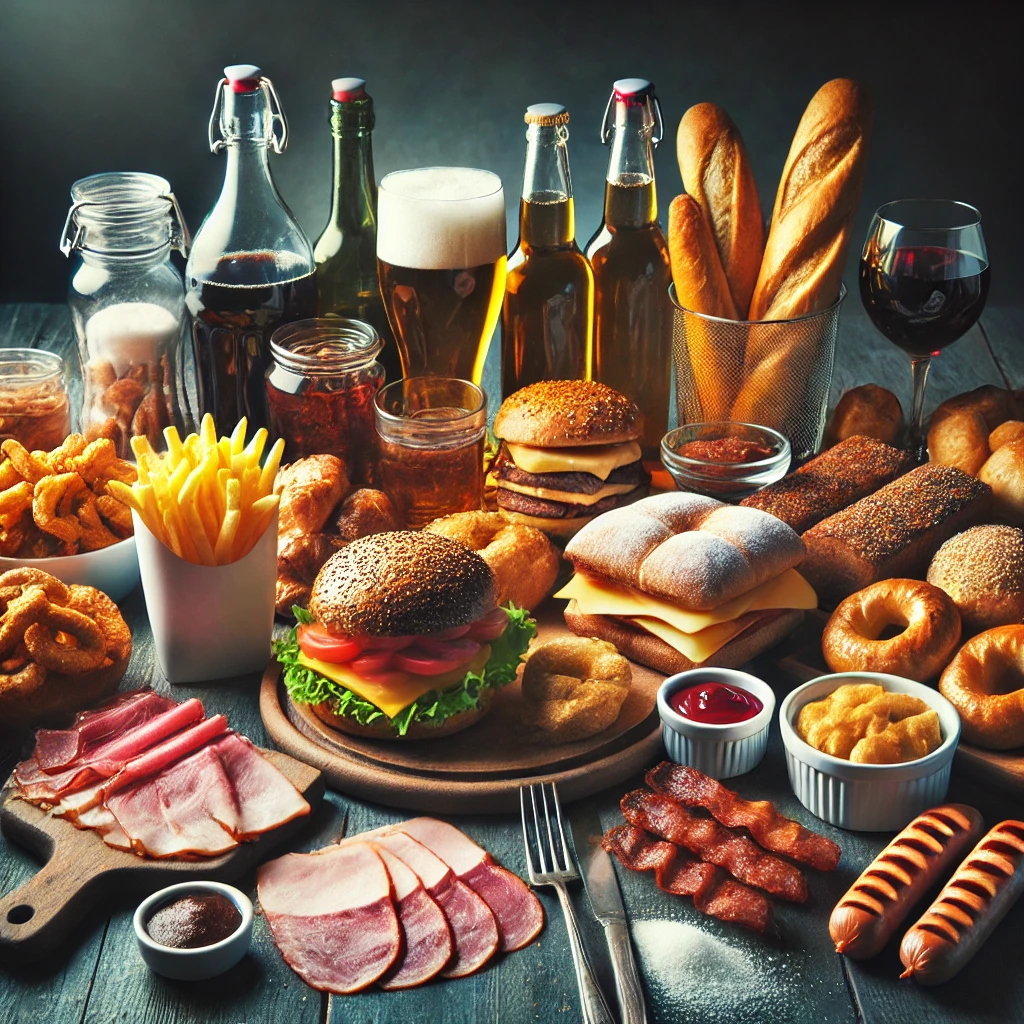

- Refined Carbohydrates: White bread, pastries, and other processed carbs can spike blood sugar levels.
- Fried Foods: French fries, fried chicken, and other deep-fried items contain trans fats.
- Sugary Beverages: Sodas and sweetened drinks contribute to inflammation.
- Processed Meats: Bacon, sausages, and deli meats are linked to increased inflammation.
- Excessive Alcohol: High alcohol intake can increase inflammatory markers.
Sample 3-Day Anti-Inflammatory Meal Plan
To help you get started, here’s a simple meal plan:
Day 1
- Breakfast: Oatmeal topped with blueberries, walnuts, and a drizzle of honey.
- Lunch: Quinoa salad with mixed greens, cherry tomatoes, cucumber, chickpeas, and a lemon-tahini dressing.
- Dinner: Grilled salmon with roasted Brussels sprouts and sweet potatoes.
- Snack: Apple slices with almond butter.
Day 2
- Breakfast: Greek yogurt with chia seeds, sliced strawberries, and a sprinkle of flaxseeds.
- Lunch: Lentil soup with carrots, celery, and spinach.
- Dinner: Stir-fried tofu with broccoli, bell peppers, and snap peas over brown rice.
- Snack: Carrot
For in-depth articles and insights on how Technology and AI are revolutionizing wellness, don’t miss out on these must-read pieces on TopBloggingHub.com: Explore Now: Technology and AI
Best Reads and References on Inflammation
For a deeper understanding of inflammation, its causes, effects, and how to manage it, check out these authoritative sources:
- Understanding Acute and Chronic Inflammation – Harvard Health Publishing
Harvard Health provides an in-depth look at inflammation, explaining how acute and chronic inflammation affect the body. - What Is Inflammation? Types, Causes & Treatment – Cleveland Clinic
A detailed guide from Cleveland Clinic covering the science behind inflammation, its symptoms, and management strategies. - Chronic Inflammation: What It Is, Why It’s Bad & How to Reduce It – Mayo Clinic
Mayo Clinic Press discusses the dangers of chronic inflammation and practical ways to combat it through lifestyle changes.