Cervical cancer is a significant health concern for women worldwide. Understanding its causes, recognizing symptoms, and knowing prevention strategies are crucial steps toward reducing its impact.

What Is Cervical Cancer?
Cervical cancer starts in the cells of the cervix—the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. It’s primarily caused by persistent infection with high-risk types of human papillomavirus (HPV).
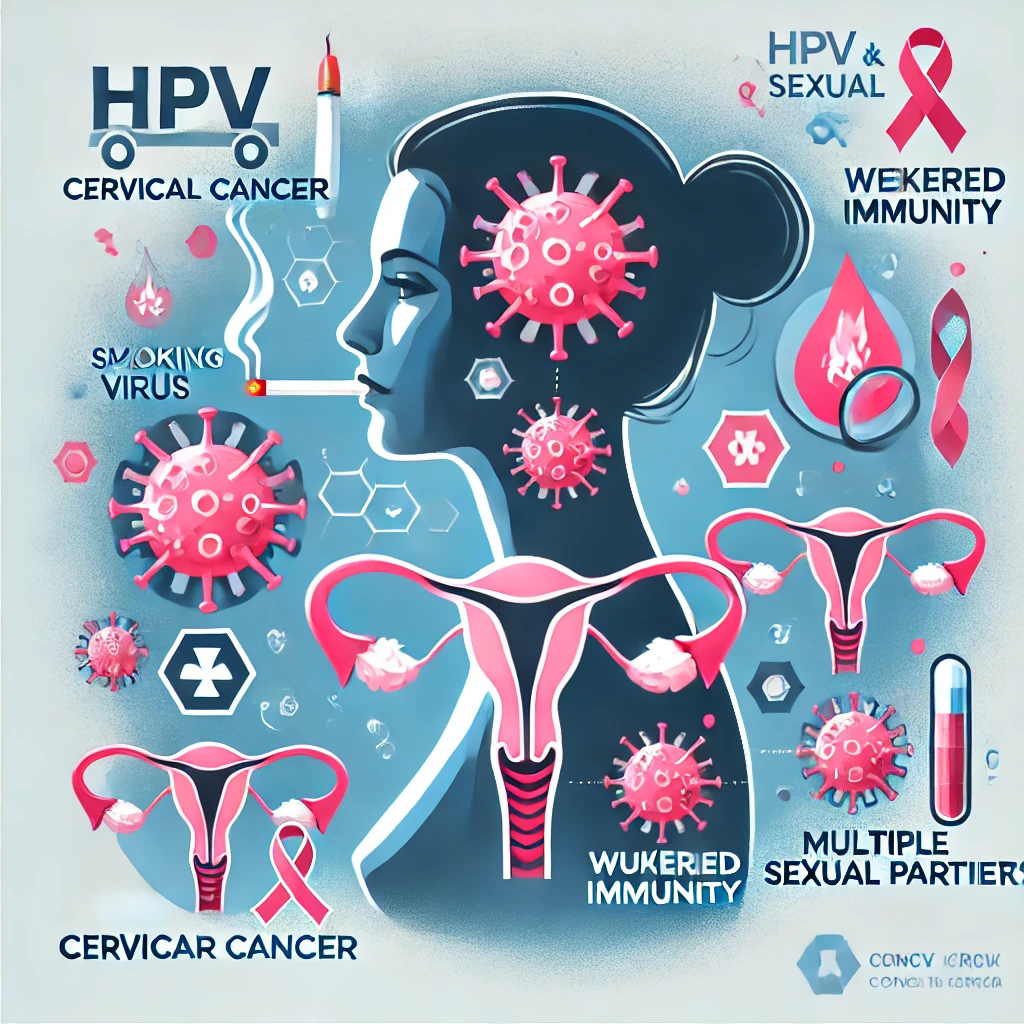
Causes and Risk Factors
The main cause of cervical cancer is a long-lasting infection with certain types of HPV. HPV is a common virus spread through sexual contact. While many HPV infections go away on their own, some can lead to cancer if not detected and treated early.
Other risk factors include:
- Multiple Sexual Partners: Having many sexual partners increases the chance of HPV infection.
- Weakened Immune System: Conditions like HIV can make it harder for the body to fight off HPV infections.
- Smoking: Smoking damages the body’s immune system, making it less effective in fighting HPV infections.
- Long-Term Use of Birth Control Pills: Using oral contraceptives for five or more years may increase the risk.
Symptoms to Watch For
Early stages of cervical cancer often have no symptoms. As the disease progresses, symptoms may include:
- Abnormal Vaginal Bleeding: Such as bleeding after sex, between periods, or after menopause.
- Unusual Discharge: A watery, pink, or foul-smelling discharge.
- Pelvic Pain: Pain during intercourse or at other times.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider promptly.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing cervical cancer involves several proactive steps:
- HPV Vaccination: Vaccines can protect against the types of HPV that most often cause cervical cancer. It’s recommended for preteens aged 11 to 12 but can be given as early as age 9 and up to age 26.
- Regular Screening: Routine Pap tests and HPV tests can detect precancerous conditions of the cervix, allowing for early treatment. Women should start getting Pap tests at age 21 and continue as advised by their healthcare provider.
- Safe Sexual Practices: Using condoms and limiting the number of sexual partners can reduce the risk of HPV infection.
- Avoid Smoking: Quitting smoking can help your immune system fight off HPV infections more effectively.

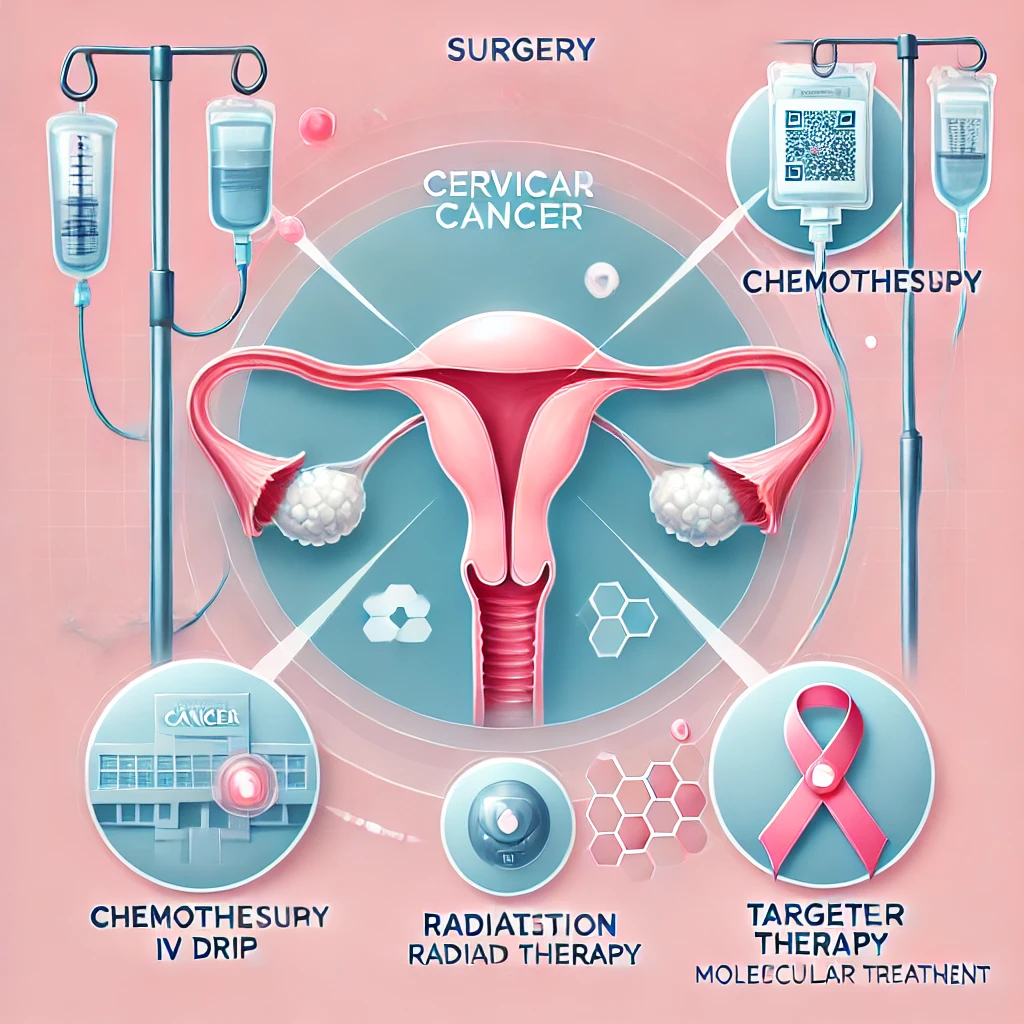
Treatment Options
Treatment for cervical cancer depends on the stage of the disease and may include:
- Surgery: Removing cancerous tissue through procedures like hysterectomy.
- Radiation Therapy: Using high-energy rays to kill cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Using drugs to destroy cancer cells.
- Targeted Therapy: Focusing on specific genes or proteins that contribute to cancer growth.
Early detection through regular screening significantly increases the chances of successful treatment.
Key Takeaways
- Get Vaccinated: The HPV vaccine is a safe and effective way to prevent cervical cancer.
- Regular Screenings Are Crucial: Early detection through Pap and HPV tests can prevent most cervical cancers.
- Practice Safe Sex: Reducing exposure to HPV can lower the risk of cervical cancer.
- Avoid Smoking: Quitting smoking strengthens your immune system to fight infections.
By taking these steps, you can significantly reduce your risk of cervical cancer. Stay informed, stay proactive, and prioritize your health.



For more detailed information, consult with your healthcare provider or visit reputable health websites.
Recommended External Links for Your Blog Post
1. World Health Organization (WHO) – Cervical Cancer Overview
https://www.who.int/health-topics/cervical-cancer
Provides global insights on cervical cancer, prevention, and treatment guidelines.
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) – HPV and Cervical Cancer
https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/cervical
Covers HPV, cervical cancer risks, prevention, and screening recommendations.
3. American Cancer Society – Cervical Cancer Guide
https://www.cancer.org/cancer/cervical-cancer.html
Includes symptoms, treatments, and latest research on cervical cancer.
Explore Our Blog – Unlock Expert Insights, Tips, and Strategies Today!
Dive into our curated collection of blog posts designed to inspire, educate, and empower you. Whether you’re seeking actionable advice, industry trends, or in-depth guides, our content is crafted to deliver 100% value. Start reading now and take the next step toward achieving your goals!