Imagine this: It’s flu season, and everyone around you seems to be catching a cold. But you? You’re feeling strong, energized, and healthy. What’s your secret? It’s not magic—it’s the power of food.
In today’s fast-paced world, maintaining a strong immune system is more important than ever. But how can you improve immunity with food? The answer lies in the nutrients you consume every day. From vitamin C-rich citrus fruits to zinc-packed pumpkin seeds, the right foods can supercharge your body’s natural defenses. This guide dives into the science of immune-boosting nutrition, offering actionable tips, global insights, and delicious recipes to help you stay healthy year-round.

Why Nutrition Matters for Your Immune System
Your immune system is your body’s defense mechanism against infections, viruses, and diseases. While factors like sleep, exercise, and stress management play a role, nutrition is the foundation of immune health.

Key Benefits of Immune-Boosting Foods
- Rich in Antioxidants: Foods like berries, spinach, and nuts combat oxidative stress, which weakens immunity.
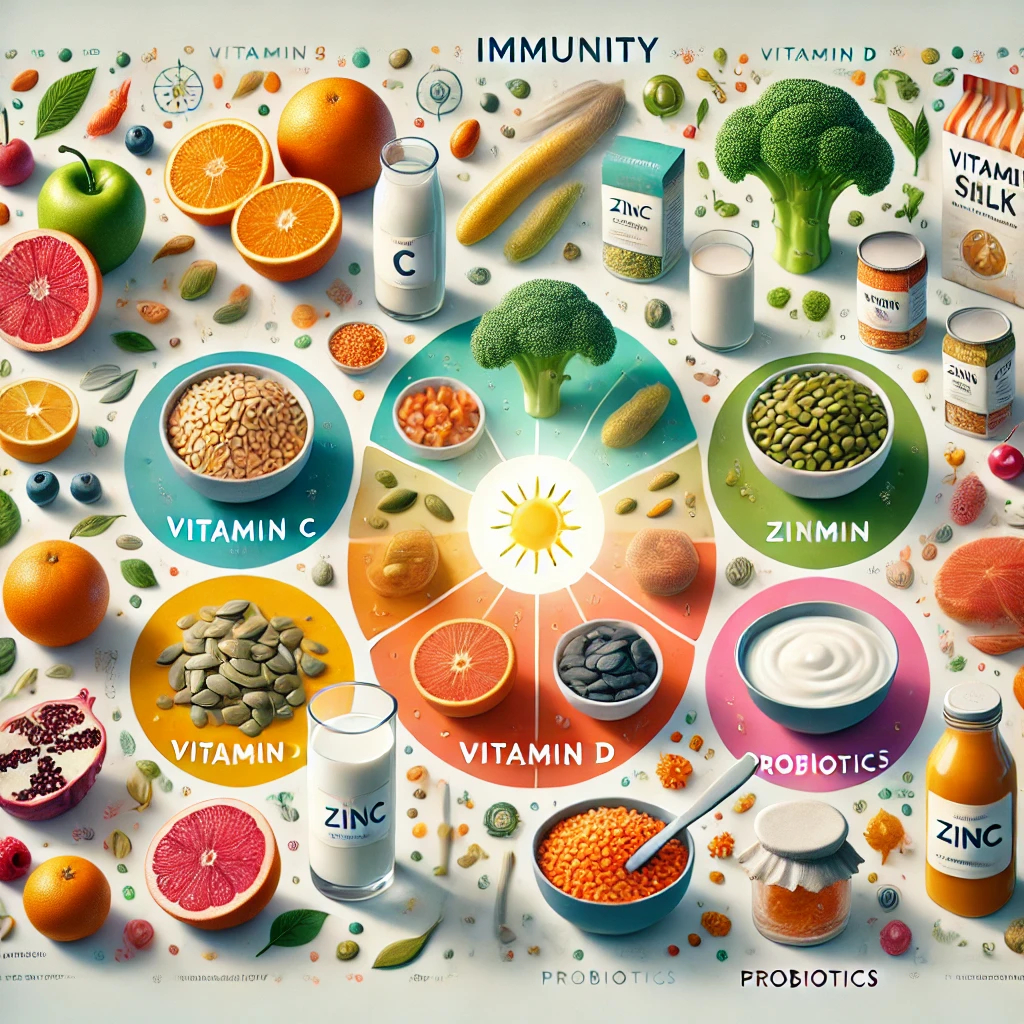
- Packed with Vitamins and Minerals: Vitamin C, zinc, and vitamin D are essential for immune function.
- Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Turmeric, ginger, and fatty acids reduce inflammation, supporting overall health.
- Gut Health Support: Probiotics in yogurt and fermented foods promote a healthy gut microbiome, which is crucial for immunity.
How to Improve Immunity with Food: A Global Perspective
1. Immune-Boosting Foods from Around the World
- Asia: Turmeric (common in Indian cuisine) contains curcumin, a potent anti-inflammatory compound.
- Mediterranean: Olive oil and fatty fish like salmon are rich in omega-3s, which support immune health.
- Latin America: Chili peppers are high in vitamin C and capsaicin, which boosts metabolism and immunity.
- Africa: Moringa, a nutrient-dense superfood, is widely used for its immune-boosting properties.

2. Localized Tips for Immune Health
While the principles of immune-boosting nutrition are universal, here are some region-specific insights:
- Tropical Regions: Incorporate citrus fruits like oranges and guavas, which are rich in vitamin C.
- Colder Climates: Focus on vitamin D-rich foods like eggs and fortified milk, especially during winter.
- Urban Areas: Combat pollution-related oxidative stress with antioxidant-rich foods like green tea and dark chocolate.
The Science Behind Immune-Boosting Foods
How Nutrients Support Immunity
- Vitamin C: Stimulates the production of white blood cells, which fight infections. Found in citrus fruits, bell peppers, and broccoli.
- Zinc: Essential for immune cell development and communication. Found in pumpkin seeds, lentils, and chickpeas.
- Vitamin D: Regulates immune responses and reduces inflammation. Found in fortified foods and sunlight exposure.
- Probiotics: Enhance gut health, where 70% of the immune system resides. Found in yogurt, kefir, and kimchi.
The Role of Phytochemicals
Phytochemicals, found in plant-based foods, have powerful immune-boosting properties. For example:
- Quercetin: Found in apples and onions, it has antiviral and anti-inflammatory effects.
- Sulforaphane: Found in broccoli and kale, it activates antioxidant pathways in the body.
Risks and Ethical Concerns in Nutrition Trends
While nutrition is a powerful tool for immune health, it’s important to approach it responsibly.
1. Misinformation and Fad Diets
- Problem: The rise of unverified health claims and extreme diets can lead to nutrient deficiencies.
- Solution: Rely on evidence-based information from trusted sources like the World Health Organization (WHO) or registered dietitians.
2. Lack of Regulation in Supplements
- Problem: Immune-boosting supplements are often marketed without proper regulation, leading to safety concerns.
- Solution: Prioritize whole foods over supplements and consult a healthcare professional before starting any new regimen.
3. Accessibility and Affordability
- Problem: Nutrient-rich foods can be expensive or inaccessible in certain regions.
- Solution: Focus on affordable, locally available superfoods like lentils, spinach, and seasonal fruits.
Future of Nutrition and Immune Health
Emerging Trends
- Personalized Nutrition: Advances in genomics allow for tailored dietary recommendations based on individual needs.
- Functional Foods: Foods fortified with immune-boosting ingredients, like probiotic-enriched snacks, are gaining popularity.
- Sustainable Diets: Plant-based and locally sourced diets are not only good for immunity but also for the planet.

Global Solutions for Better Nutrition
- Education: Governments and NGOs can promote nutrition literacy through campaigns and school programs.
- Policy Changes: Implementing regulations to ensure food safety and affordability, such as subsidies for nutrient-rich crops.
- Technology: Apps and platforms that provide personalized meal plans and track nutrient intake.
FAQs: How to Improve Immunity with Food
1. What are the best foods to boost immunity?
Citrus fruits, leafy greens, nuts, seeds, yogurt, and turmeric are excellent choices.
2. Can supplements replace immune-boosting foods?
While supplements can help, whole foods provide a broader range of nutrients and are generally more effective.
3. How long does it take to see results from dietary changes?
Consistent dietary improvements can show results in as little as 2-3 weeks, but long-term habits yield the best outcomes.
4. Are there any foods that weaken immunity?
Processed foods, sugary snacks, and excessive alcohol can suppress immune function.
5. How can I make immune-boosting meals on a budget?
Focus on affordable staples like lentils, oats, seasonal vegetables, and eggs.
Conclusion
Improving your immunity with food is not just about eating the right things—it’s about making sustainable, informed choices that support your overall health. From turmeric-laden curries to Mediterranean-inspired salads, the world is full of delicious, immune-boosting options.
So, what’s your favorite immune-boosting food? Share your thoughts in the comments below, and let’s build a healthier world together!
External Links for SEO and AEO
- World Health Organization (WHO) – Nutrition
- Harvard School of Public Health – The Nutrition Source
- National Institutes of Health (NIH) – Zinc and Immune Health
For more health and wellness tips, check out TopBloggingHub.com for in-depth articles.


This is a crucial subject—keep producing such remarkable content! Someone shared their personal weight loss story, highlighting the difficulties they encountered before discovering the Diet-To-Go Meal Service. They noted that the pre-portioned meals saved them time and supported their commitment to their goals. The conversation is a reminder of how essential balance is to the weight loss journey. For those who may find it useful, here’s the link they provided.