What Is Anemia?
Anemia is a condition where your body lacks enough healthy red blood cells to carry oxygen efficiently. This leads to fatigue, weakness, and other health complications. Understanding what causes anemia is the first step in managing and preventing it effectively.
What Are the Main Causes of Anemia?
Anemia can result from various factors, including nutritional deficiencies, medical conditions, and genetic disorders. Let’s explore the primary causes:
1. Iron Deficiency – The Most Common Cause
Iron is essential for producing hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen. Without enough iron, your body can’t make sufficient hemoglobin, leading to anemia.
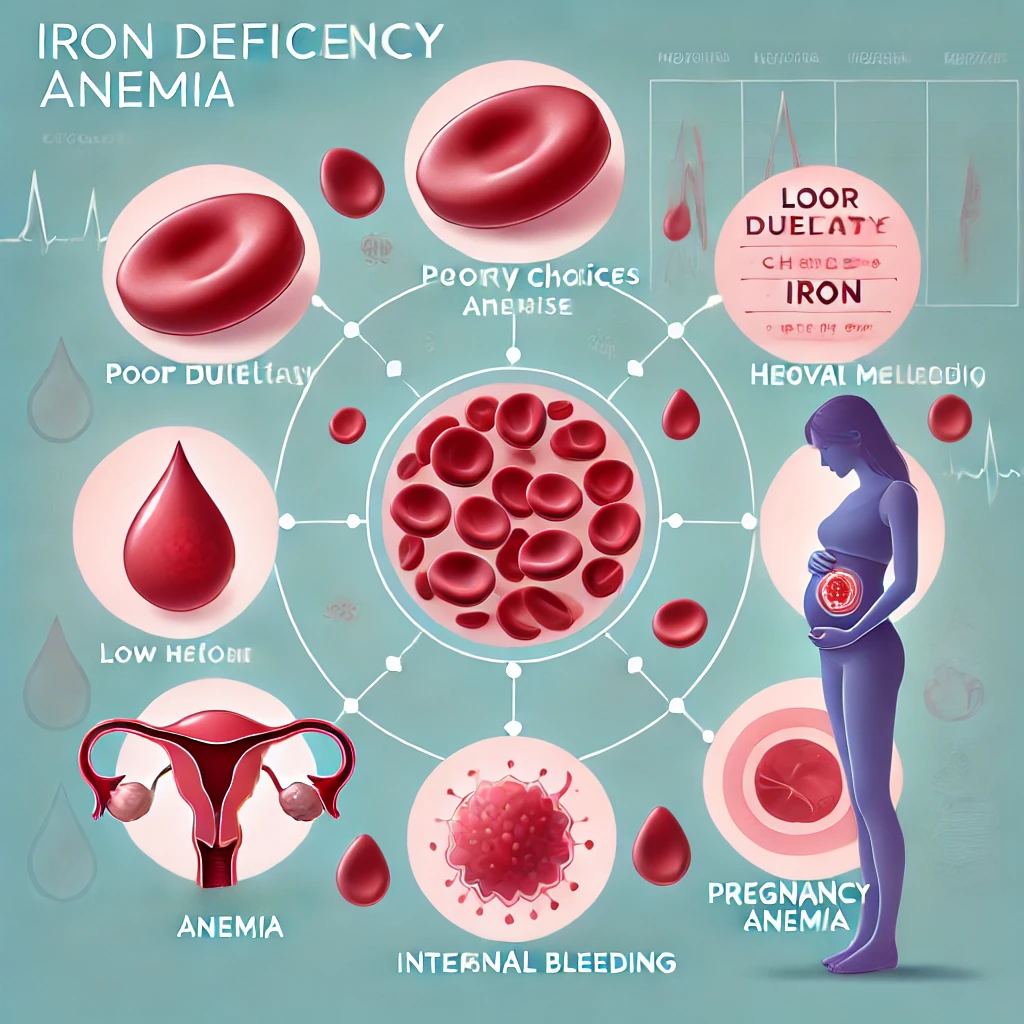
Causes of Iron Deficiency Anemia:
- Poor dietary intake of iron-rich foods
- Blood loss due to heavy menstruation
- Internal bleeding from ulcers or colon polyps
- Pregnancy and childbirth

Prevention Tips: ✔ Eat iron-rich foods like spinach, lentils, and red meat.
✔ Take iron supplements if recommended by a doctor.
✔ Pair iron sources with vitamin C for better absorption.
2. Vitamin Deficiencies – B12 and Folate Deficiency Anemia
Vitamins like B12 and folate are crucial for red blood cell production. A deficiency can lead to megaloblastic anemia, where cells grow abnormally large and inefficient.
Causes of Vitamin Deficiency Anemia:
- Poor diet lacking in B12 and folate
- Malabsorption conditions like Crohn’s disease
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Certain medications interfering with vitamin absorption
Prevention Tips: ✔ Eat fortified cereals, dairy products, and leafy greens.
✔ Take vitamin B12 injections or supplements if needed.
✔ Reduce alcohol consumption for better nutrient absorption.
3. Chronic Diseases That Cause Anemia
Several chronic illnesses can interfere with red blood cell production, leading to anemia of chronic disease.
Common Conditions:
- Kidney disease
- Cancer
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Inflammatory bowel disease
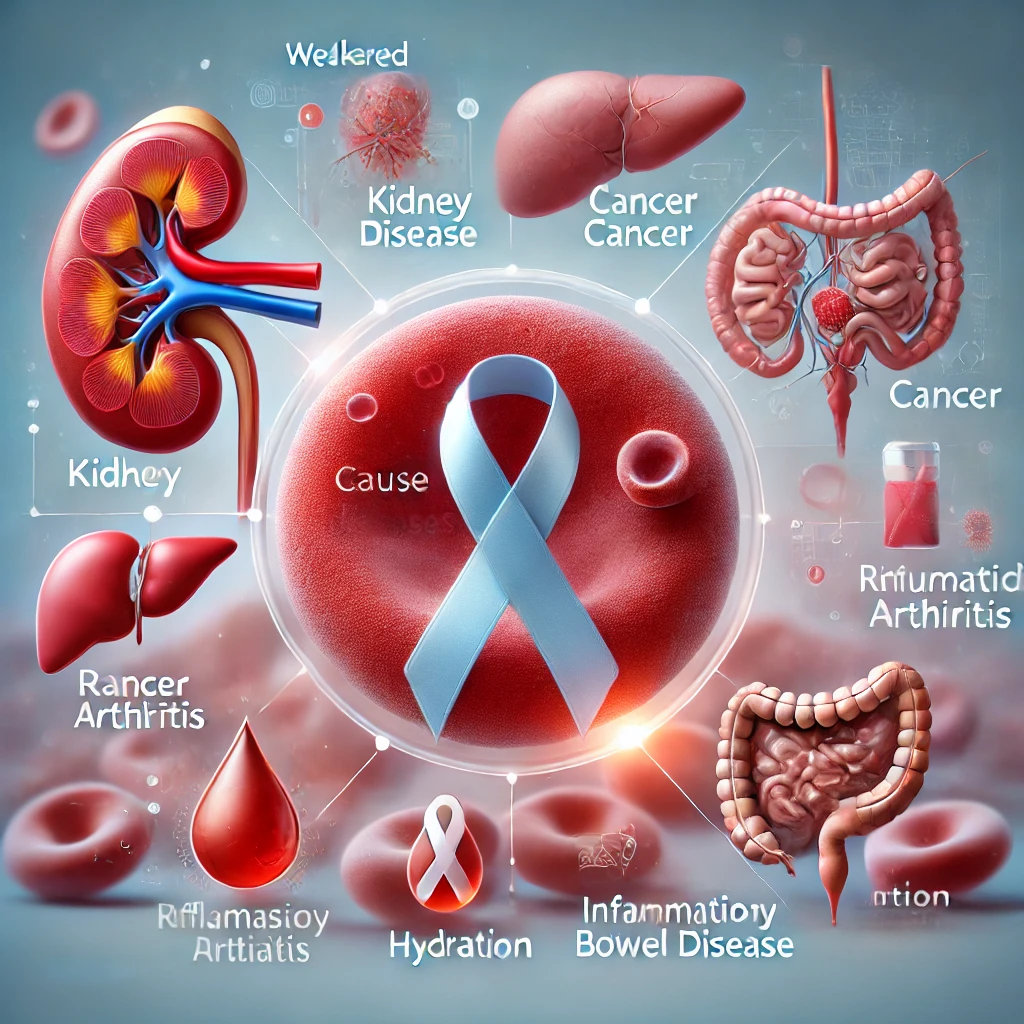
Prevention Tips: ✔ Manage underlying conditions with medical guidance.
✔ Follow a balanced diet to support overall health.
✔ Stay hydrated and active.
4. Genetic Disorders – Sickle Cell & Thalassemia
Some forms of anemia are inherited, meaning they are passed down through families.
Types of Genetic Anemia:
- Sickle Cell Anemia: Causes misshapen red blood cells, leading to poor oxygen transport.
- Thalassemia: Affects hemoglobin production, resulting in fewer healthy red blood cells.
Management Tips: ✔ Regular check-ups to monitor blood health.
✔ Specialized treatment plans from a healthcare provider.
✔ Bone marrow transplants in severe cases.
5. Blood Loss – A Hidden Culprit
Excessive blood loss reduces red blood cells, leading to anemia.
Causes of Blood Loss Anemia:
- Heavy menstrual periods
- Surgery or trauma-related bleeding
- Gastrointestinal bleeding from ulcers
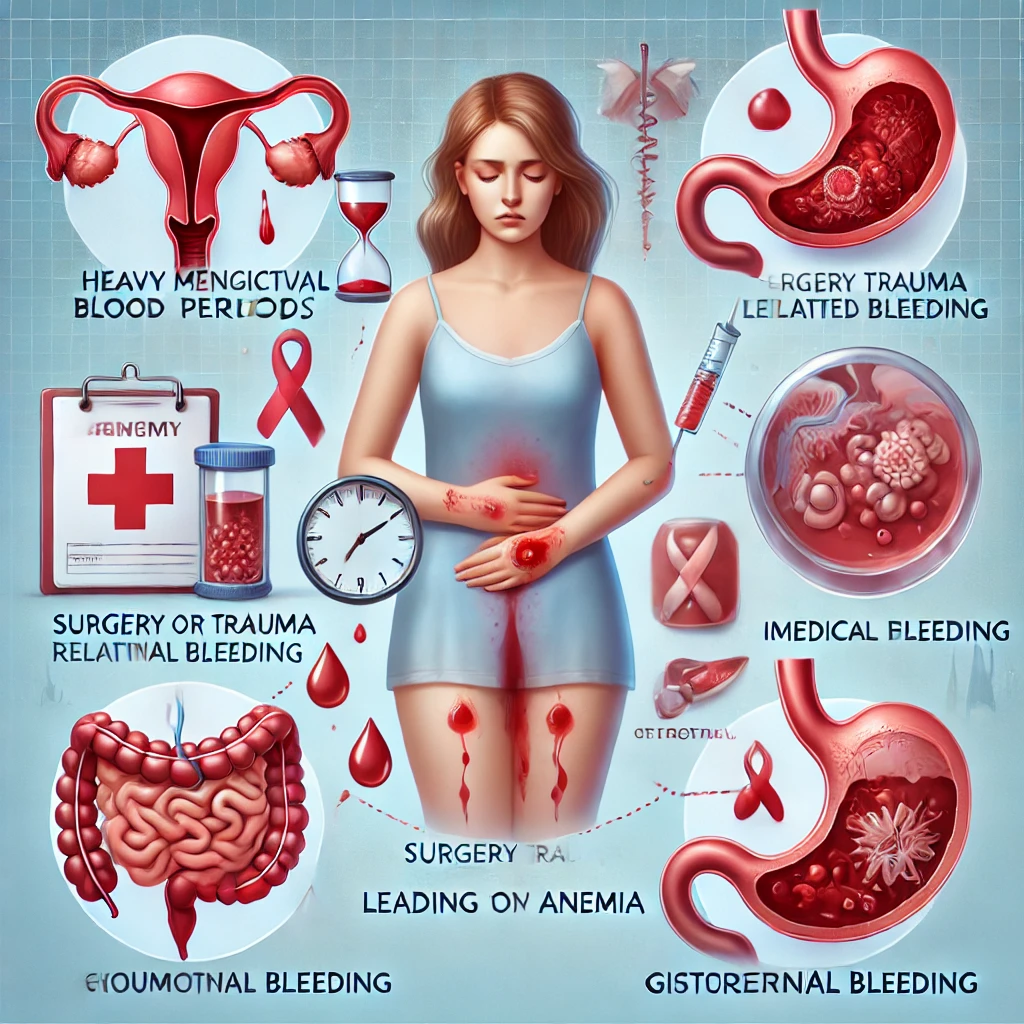
Prevention Tips: ✔ Seek medical help for excessive menstruation.
✔ Monitor and treat underlying digestive issues.
✔ Maintain a healthy diet to replenish lost blood.
Symptoms of Anemia You Shouldn’t Ignore
Anemia can go unnoticed until it worsens. Watch out for these symptoms:
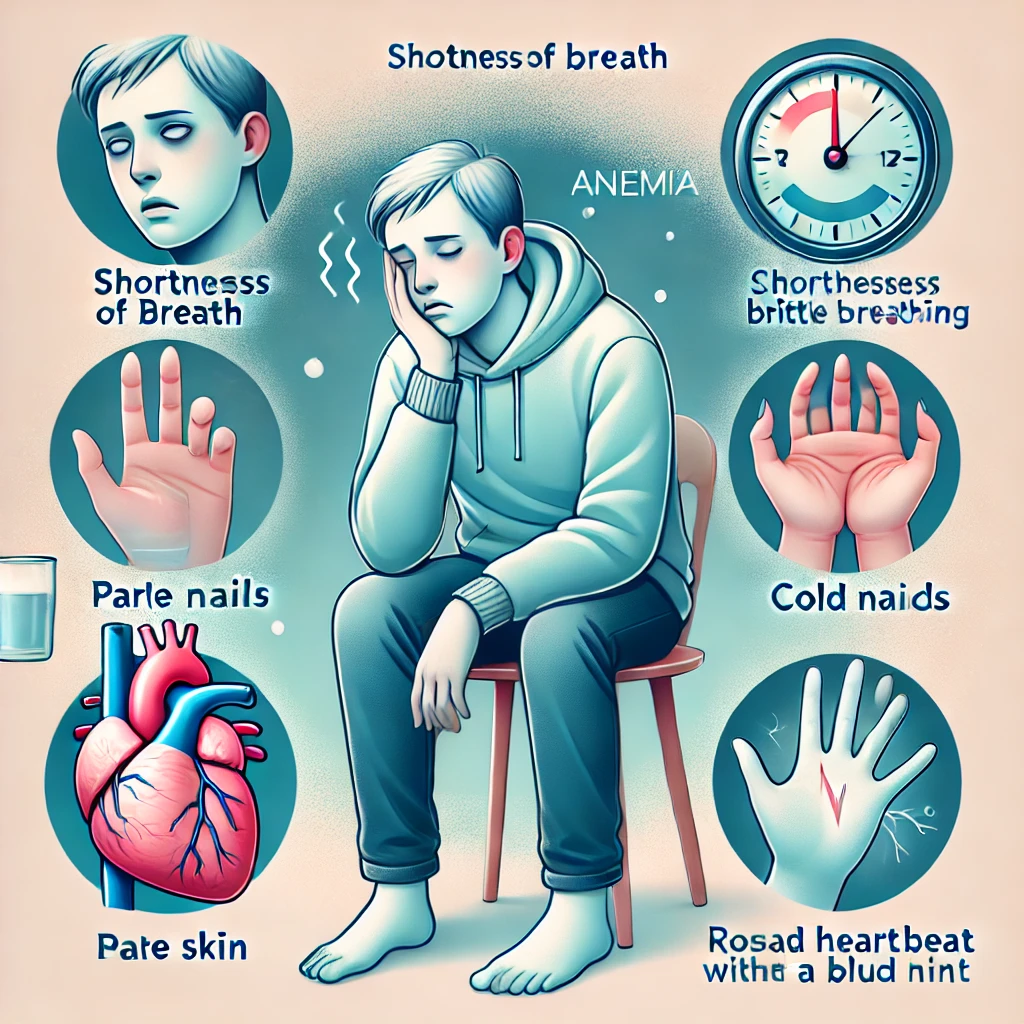
- Persistent fatigue and weakness
- Shortness of breath and dizziness
- Pale skin and brittle nails
- Cold hands and feet
- Rapid heartbeat or chest pain
If you notice these signs, consult a doctor for a blood test.
How to Prevent Anemia Naturally
Prevention is always better than cure. Follow these strategies:
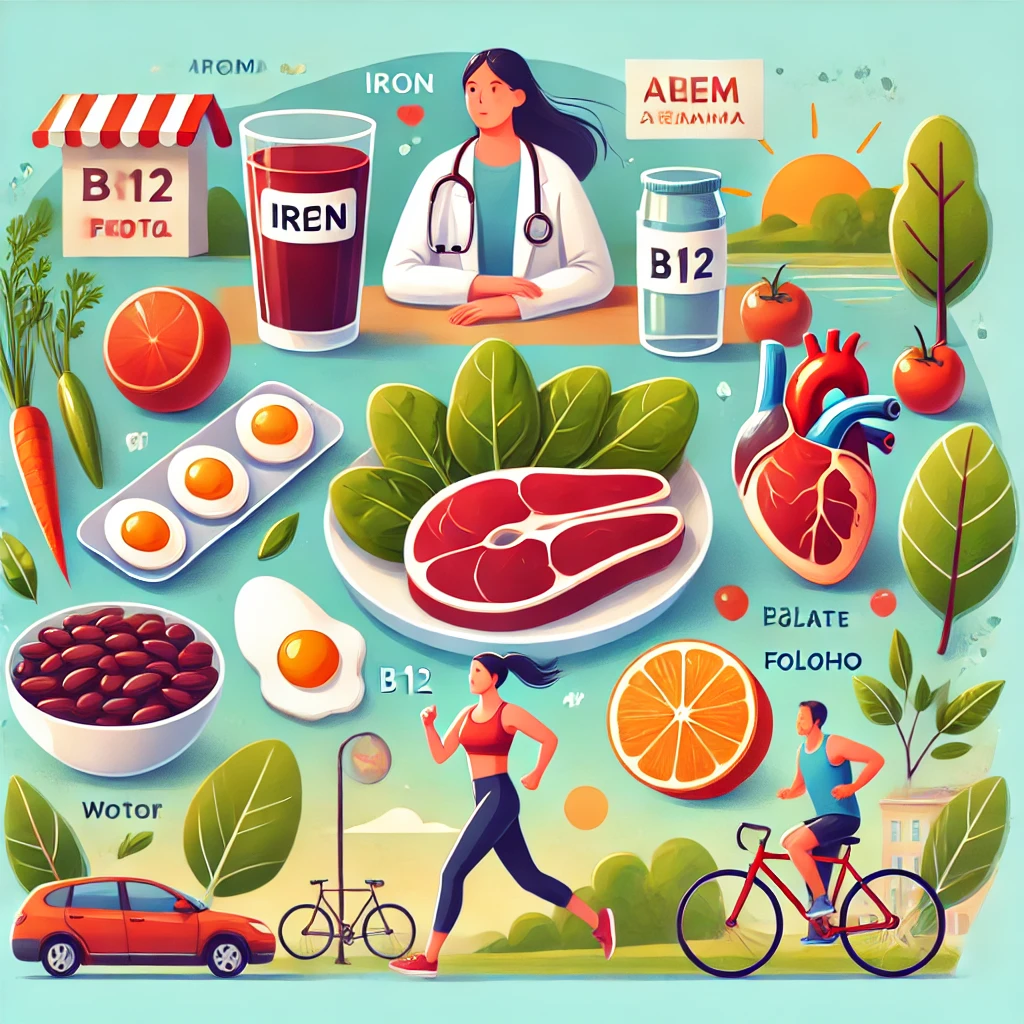

- Eat a nutrient-rich diet with iron, B12, and folate.
- Avoid excessive caffeine and alcohol, which hinder iron absorption.
- Stay hydrated and get regular exercise to boost circulation.
- Monitor underlying health conditions and seek timely treatment.
FAQs About Anemia Causes
1. Can stress cause anemia?
Stress alone does not cause anemia, but chronic stress can affect nutrient absorption and immunity, indirectly leading to anemia.
2. Is anemia more common in women?
Yes, women are more prone to anemia due to menstruation, pregnancy, and hormonal changes.
3. Can anemia be cured completely?
It depends on the cause. Nutritional anemia can be reversed with proper diet and supplements, but genetic anemia requires long-term management.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the causes of anemia helps in early detection and prevention. By maintaining a balanced diet, staying active, and addressing underlying health issues, you can keep anemia at bay.
For more health and wellness tips, check out TopBloggingHub.com for in-depth articles.
For medical references, visit Mayo Clinic.